When we age, the structure of the skin changes over time. Usually, this manifests with skin experiencing a loss of volume, sagging skin in various areas of the body and deepening wrinkles which all typically happen by our 40s. This is due to a combination of internal process and external factors.
Why does sagging skin occur?
The ageing process is partly due to our genetics, along with a combination of external factors such as environmental and lifestyle factors. Intrinsic ageing combines these factors to trigger the slowing down of key processes and functions in the skin.
Moreover, it is this slowing down of ageing that causes the most visible signs of ageing: skin sagging and a loss of volume/facial contours, fine lines & wrinkles, a loss of elasticity and a loss of radiance in the skin. The wrinkles above the mouth, nasolabial folds, are also linked to a loss of volume.
Identifying a loss of volume and facial contours can be difficult, at least initially, so look out for the following signs:
- Lipstick starting to bleed on the lips
- Skin sagging in the face
- Flattening of the cheeks
- Neck lines or 'turkey neck'
Unfortunately, these symptoms can impact the overall look of the face, giving a tired or sad appearance, but there are ways to manage sagging skin.
What causes sagging skin?
As we age, there are many factors that cause sagging skin, in various areas of the body.
Saggy or skin sagging can happen almost anywhere on the body, and typically happens when the skin loses the ability to adjust back into place normally as we age. Common areas where you might see sagging skin include:
- Upper arms
- Face and jawline
- Neck/throat
- Jowls
- Inner thighs
- Chin
- Eyelids
- Abdomen
Skin sagging can be caused of several factors:
Ageing
As the skin ages, it loses two vital proteins produced in the dermis – elastin and collagen.
Elastin is a protein that gives the skin elasticity, which provides firm skin with the ability to bounce back when stretched.
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the body and is produced by fibroblasts. When skin is firm, this is due to collagen. Collagen is made of strong fibres, which helps the skin maintain its structure and firmness, as well as strength and support throughout your body. When preventing skin sagging, collagen plays an especially significant role in doing so.
As we age, the production of elastin and collagen declines, which then reduces firm skin significantly. This is a normal part of ageing, although, these two proteins can also be affected by external factors over time.
Lifestyle
As with general skin ageing, external lifestyle factors can impact our skin and cause wrinkles, loss of elasticity and sagging skin. These factors include:
Sun exposure: Sagging skin can be more likely if you are exposed to more sunlight and not taking care of your skin or health, which can make your skin look saggy and wrinkly at a younger age. Spending too much time in the sun can compromise skin structure, damage collagen and cause photoageing (premature ageing of the skin caused by the sun).
Smoking: Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes/tobacco further degrade skin collagen
These lifestyle factors combine to cause oxidative stress. This occurs when molecules known as ‘free radicals’ are formed internally and attack cellular structures including those that help the skin look smooth and firm. Once the structure is weakened, and collagen and functional elastin decline, skin ageing is accelerated. The visible signs including fine lines and wrinkles, a loss of volume, sagging skin, a loss of elasticity and less radiance appear on skin’s surface.
Hormonal changes
In puberty, oestrogen levels are high. Skin is smooth and elastic, and the skin contours are defined. As we age, hormone levels decline, and volume-giving cells decrease in both size and number leading to a loss in volume and less defined facial contours. Itchy skin can also be a symptom during menopause.
Pregnancy
Saggy or skin sagging after pregnancy is very common and may result in less firm skin. This may be more prominent for women who carry multiples such as twins or triplets, as they may see more sagging skin around the abdomen than those who only carry one baby. Dry skin can also be more prominent during pregnancy alongside skin sagging.
Signs & symptoms of sagging skin
How do I recognise sagging skin and a loss of volume?
The triangle of beauty
A visual reference such as ‘the triangle of beauty’ clearly shows how a loss of volume changes the shape and structure of the face in several subtle but transformative ways.
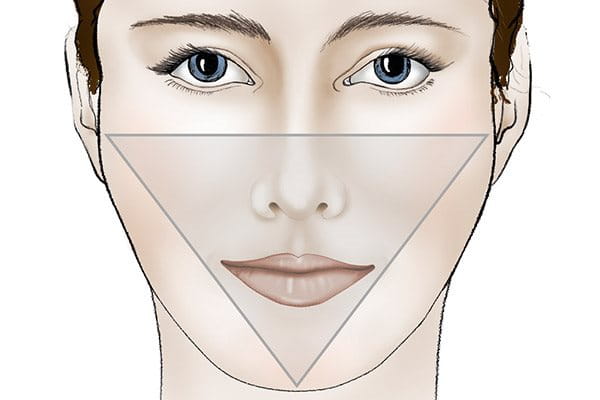
The even distribution of volume in our facial skin when we are young helps it to look attractive. The main features of a younger looking face can be clearly seen as part of the ‘triangle of beauty’. These include:
- High cheekbones
- Full jowls
- Smooth skin
- A lean, well-defined jawline
These features combine to create a face shape and structure that is wider at the top, tapering down to the narrowest point at the chin. The overall look is relaxed and positive.
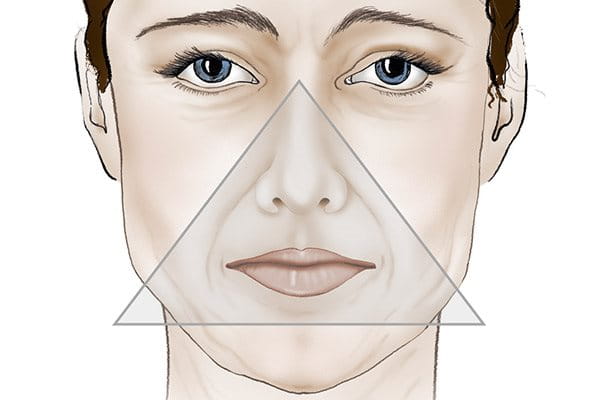
As we age, the signs of a loss of volume mean the triangle is inverted. This is due to the following changes:
- A wider, slacker jawline
- Sagging skin resulting in less defined facial contours
- Flatter cheeks
- Wrinkles on the forehead and brows
- Wrinkles around the eyes, known as crow's feet, begin to deepen
- The corners of the mouth point downwards and causes marionette lines
- Hollowness of under eye area and temples
It’s the combination of these factors that equates to an aged appearance and sagging skin on the face. As is seen here, the triangle is now turned upside down with the wider area towards the bottom of the face. As volume diminishes and skin sags the perception of the face is altered. The person can look sad or stressed and this can lead to incorrect judgements on their mood or outlook.
Contributing Factors
What processes take place within skin as it loses volume?
A gradual drop in the ‘filler’ substances that keep skin looking firm and feeling smooth lead to a loss of volume, less defined contours and sagging skin in the different layers of skin:
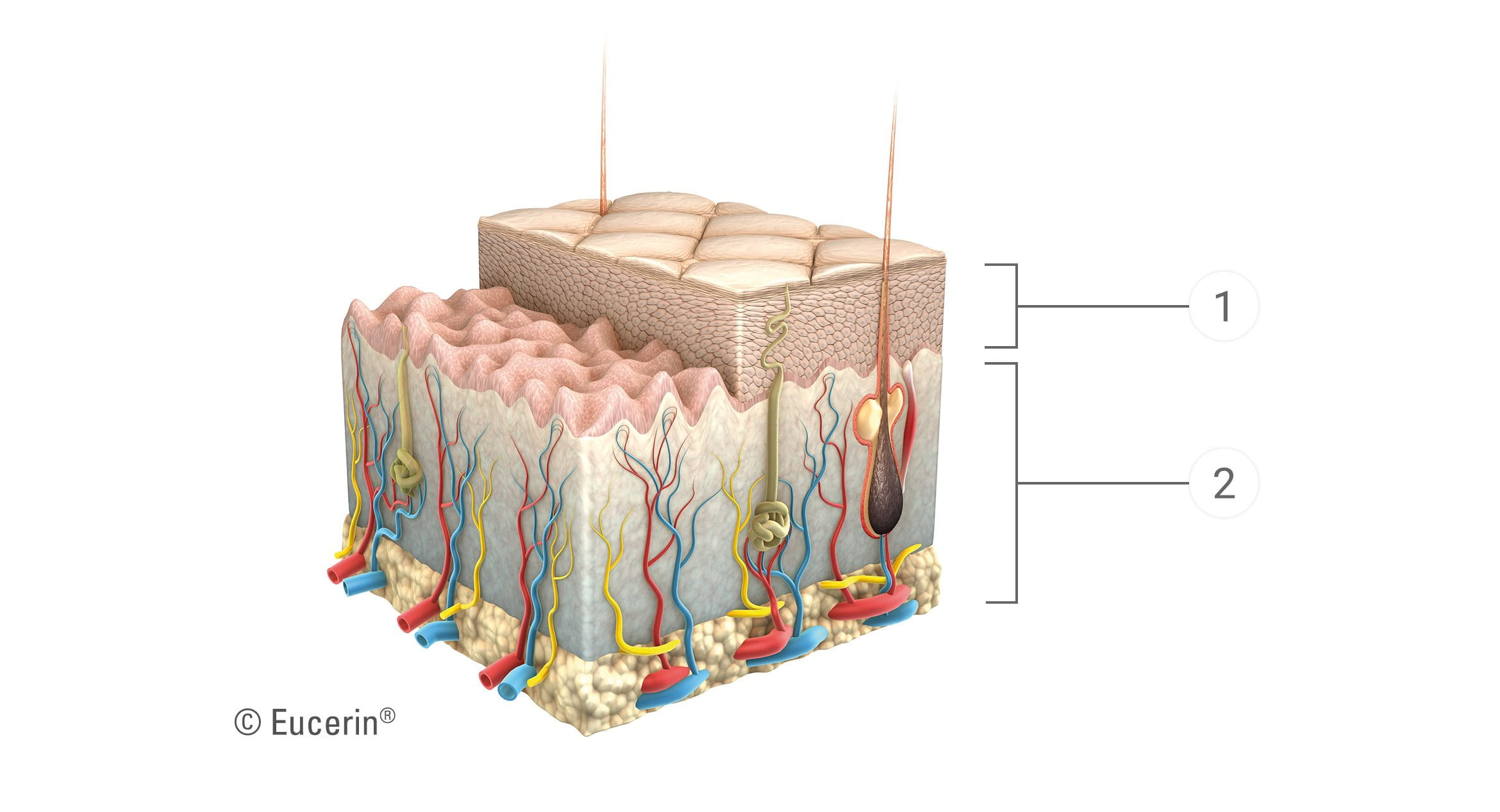
The epidermis. As we age, the outermost layers of skin produce less hyaluronic acid and fewer lipids. Skin is less able to bind in moisture, becomes drier and, as a result, fine lines and wrinkles appear. Skin starts to sag, appears thinner and its texture may be dry and rough.
The deeper layers of the skin. A 1% annual loss of collagen worsens the thinning effect together with a declining level of functional elastin. As elastin is partly responsible for the skin’s elasticity and strength, a decrease in these two substances together results in a sagging, less elastic skin. The volume-giving cells that keep skin `filled out’ reduce in size and number, leading to a shrinking of these layers. The result is a more drawn and sunken look to the skin, with flattening of the cheeks.
Over time, the blood flow delivering nutrients slows, resulting in dullness and a tendency towards dehydration and slower healing. Skin undergoes a further loss of elasticity and deep wrinkles start to form.
Treatment options for sagging skin
Although a loss of volume is a complex concern and is in many ways inevitable, the visible effects can be treated in a variety of ways to tighten skin.
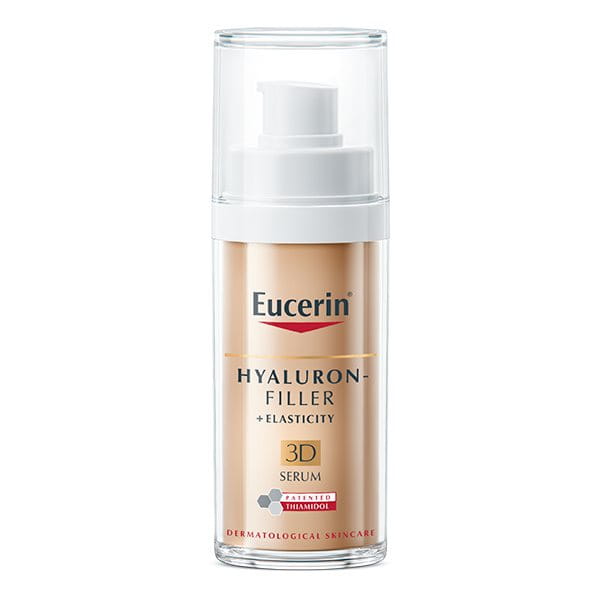
Anti-age creams can help to restore lost volume and tighten skin. A daily face care routine can enhance firmness and elasticity in the skin, while also reducing the effects of ageing and skin sagging. The Eucerin Hyaluron Filler + Elasticity range provides various creams and a serum to help re-energise collagen production and fill in wrinkles.
Ingredients to help skin sagging


The following active ingredients (listed alphabetically) are used in anti-ageing formulas to address the causes of skin sagging, loss of volume and poorly defined facial contours.
Arctiin is a naturally-derived active ingredient extracted from the fruit of the Burdock plant with anti-inflammatory and anti-ageing properties.
Arctiin strengthens the connective tissue by increasing the production of the main extracellular matrix components collagen and hyaluronic acid, as well as inhibiting the degradation of elastase. Additionally, Arctiin has anti-inflammatory properties. The Arctiin in the Eucerin Hyaluron-Filler + Anti-Age Body Cream helps boost collagen renewal, improving elasticity and firming skin on the body.
Hyaluronic Acid is formed by skin cells and is part of the connective tissue of the skin. One of its key functions is to retain moisture, and it has the ability to bind in between 1,000 and 10,000 times its own weight in water (i.e. one gram binds between one and ten liters). As we age, the skin’s natural ability to produce Hyaluronic Acid decreases and wrinkles start to form and deepen.
Dermatological treatments
To reduce sagging skin, you may be recommended to undergo non-invasive to mild invasive procedures, or for more significant sagging, an invasive treatment may be better for you. If you remain concerned about a loss of volume in your skin your dermatologist may recommend one of the following treatments:
Non-invasive treatments
- Thermowaves: Radio frequency technology is used to heat the deep collagen layers of the skin. This heat promotes the production of new collagen and tones existing collagen. The aim is to restore poorly defined facial contours.
- Ultrawaves: This treatment uses ultrasound to lift, tone and tighten sagging skin.
Mildly invasive treatments
- Fillers: Injectables are used to temporarily replace volume and give instant, short-term results. Usually used on the cheeks, temples and lips or under the eyes. Injectable Hyaluronic Acid can also help with wrinkles.
- Laser therapy: Multiple types of laser therapy treatments aim at boosting collagen production and firming of the skin. This is best utilised when additional courses of treatment are carried out and can be beneficial for reducing skin sagging of the upper arms and stomach, as well as other parts of the body.
Invasive treatments
- Fat transfer: This method involves surgically removing fat from one area of the body and transplanting it to another. It is most commonly used to replace volume in the cheeks and results are long-lasting. Swelling is not unusual and the treatment usually requires a period of downtime.
Our brand values

We deliver a holistic dermo-cosmetic approach to protect your skin, keep it healthy and radiant.

We work together with leading dermatologist and pharmacist partners around the world to create innovative and effective skincare products they can trust and recommend.

For over 100 years, we have dedicated ourselves to researching and innovating in the field of skin science. We believe in creating active ingredients and soothing formulas with high tolerability that work to help you live your life better each day.