Seborrheic (pronounced seb-o-ree-ik) Dermatitis is a common, chronic and embarrassing, skin condition typically causing yellowish scales on the scalp or face, though it can also affect other areas. Correct and frequent use of specially formulated hair and skin products can control this lifelong condition.
What is Seborrheic Dermatitis?
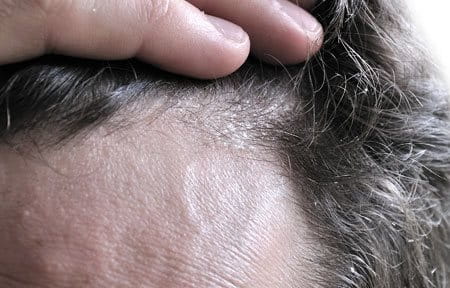

Seborrheic Dermatitis, also spelt as Seborrhoeic Dermatitis or referred to as Seborrheic Eczema, is the medical condition which, in many cases, is the underlying cause of dandruff. It is not contagious or caused by poor hygiene.
It most commonly affects adults between the ages of 30-60 and infants under 3 months, where it appears as cradle cap.
Up to 50% of the adult population suffer from dandruff with flaky, yellowish scales on the scalp and a significant number also from an inflammatory scalp condition.
In infants Seborrheic Dermatitis is known as cradle cap or crib cap. It's a temporary skin condition and should disappear as the child gets older, usually by the age of 3.

Commonly occurring symptoms of Seborrheic Dermatitis consist of:
- Skin scales – white and flaking, or yellowish, oily, and adherent – known as dandruff
- Lesions in the skin
- Plaques that cover a large area of the skin
- Skin that is oily or greasy
- Itchy skin – this may become severe if the skin becomes infected, leading to further itching and potentially bleeding if scratched
- Mild redness
- Hair may fall out
Sebborrheic Dermatitis symptoms
On the body, Seborrheic Dermatitis can appear where there are a lot of oil-producing (sebaceous) glands like the upper back, nose, scalp or oily skin patches inside the ear.
Other commonly affected areas include the eyebrows and eyelids, the nose nasolabial folds, and middle of the chest. It is often accompanied by reddened skin.
For infants, symptoms are thick, crusty, yellowish flakes of skin from over the infant's scalp, and sometimes the eyes, ears, and nose.
Seborrheic Dermatitis causes
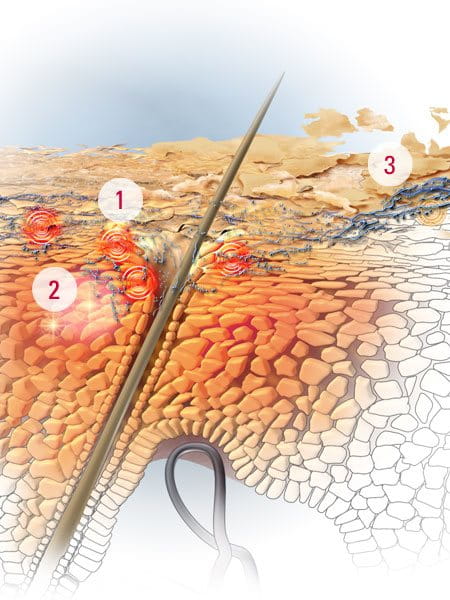
Seborrheic Dermatitis occurs when the scalp’s cell renewal process shortens, leading to the rapid shedding of horny skin cells, which stick together to form visible flakes. This process has been linked to many causes. It has been noted to be hereditary, with children of affected people more likely to be affected.
However, it is also known to be linked to irritation from a yeast called malassezia, which thrives in areas of skin which are very oily, and causes microinflammations which lead to skin and scalp itchiness.
Other factors such as physical or emotional stress, hormonal changes, poor diet or alcohol intake, fatigue, weather extremes, infrequent use of shampoo, poor skin cleansing, and obesity may increase the risk. Neurologic conditions, including Parkinson's disease, head injury, and stroke may be associated with Seborrheic Dermatitis. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) has also been linked to increased cases of Seborrheic Dermatitis.
Seborrheic Dermatitis treatment
The best way to reduce the severity of Seborrheic Dermatitis is by paying careful attention to scalp and skin care. Specially formulated shampoos help to remove the flakes of skin and also prevent the reformation of flaky skin.


Shampoos designed specifically for Seborrheic Dermatitis usually include any of the following actives; Climbazole, Piroctone Olamine, Polidocanol, anti-inflammatory agents such as salicylic acid and resorcin, minerals such as zinc or selenium sulphide, or antifungals like ketoconazole.
The following Eucerin products are specifically designed for dry or greasy dandruff and are dermatologically proven to be effective for Seborrheic Dermatitis treatment:
- Eucerin DermoCapillaire
- Eucerin DermoCapillaire Urea Shampoo
- Eucerin DermoCapillaire Urea Scalp Treatment
In severe cases, a dermatologist or doctor may prescribe an antifungal, such as ketoconazole, metronidazole, or azelaic acid, which affects the malassezia yeast, or lotions containing anti-inflammatory corticosteroids.
More recently, topical immunomodulators such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus have been used.
Seborrheic Dermatitis is a chronic condition that can be managed well with the right treatment. It often has flare-ups between extended periods of inactivity. A more extreme form of this condition overlaps with Psoriasis of the scalp and is called Sebopsoriasis.
Attention
Always consult a dermatologist if Seborrheic Dermatitis symptoms do not respond to frequent use of medicated shampoos. Also call if patches of Seborrheic Dermatitis become infected, fluid or pus appears, crusts form, or it becomes very red or painful.
Our brand values

We deliver a holistic dermo-cosmetic approach to protect your skin, keep it healthy and radiant.

For over 100 years, we have dedicated ourselves to researching and innovating in the field of skin science. We believe in creating active ingredients and soothing formulas with high tolerability that work to help you live your life better each day.

We work together with leading dermatologist and pharmacist partners around the world to create innovative and effective skincare products they can trust and recommend.