The skin is one of our most important organs, as it protects us against the environment, gives us our appearance and sense of touch. However, when skin becomes dry, it can feel rough and tight, or even become chapped or itchy, and its ability to function properly becomes compromised.
Signs & Symptoms
Dry facial skin
Dry skin on the face, not to be mistaken for psoriasis on the face, is particularly uncomfortable and may lead to premature ageing. The dryness usually appears on the cheeks under the jaw and around the eyes. The lips often also become dry, especially in winter.
Dry skin on the body
Dry skin on the body most frequently occurs first on the feet and shins, as these areas have less sebaceous glands and are often more exposed to the environment, although it can occur anywhere on the body.
Dryness is a leading cause of skin complaints
A lack of moisture within the skin can present in different ways, ranging from typical roughness, scaling, and small cracks to redness, inflammation, constant tightness and itching. However, this will differ depending on the severity and location of dryness.
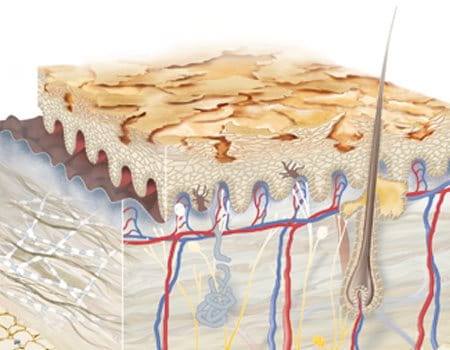
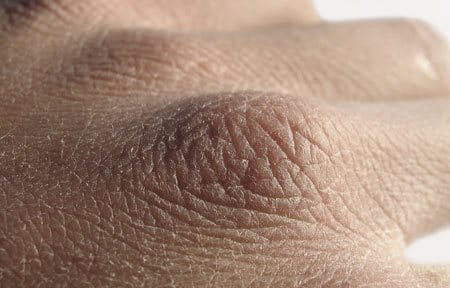
Symptoms of dry skin
Initially, when the skin first begins to lose moisture, the skin feels:
- Tight
- Rough
Symptoms of very dry skin
If the dryness is not treated, and the skin loses further moisture, the skin becomes:
- Very tight
- Scaly
- Chapped
- Itchy
Symptoms of rough and cracked skin
Certain areas of the body, particularly hands, feet, elbows and knees are prone to:
- Extreme tightness
- Extreme roughness
- Skin cracks or fissures
- Intense itching
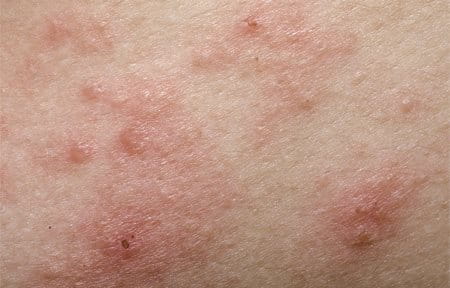
Dry skin can also be related to certain diseases
Xerosis is the medical term for dry skin. It comes from Greek; ‘Xero’, means ‘dry’, and ‘osis’ means ‘disease’.
Atopic Dermatitis and psoriasis are also linked to dryness and can show other symptoms like inflammation and intensive itchiness. They tend to be genetically linked.
Metabolic conditions such as, diabetes mellitus and kidney diseases can also have an influence on skin moisture content and may be accompanied by severe skin dryness.
The relationship between dry and sensitive skin

Dry skin is usually sensitive, and might react with irritation if in contact with harsh detergents, soaps or unsuited cosmetic products. When the skin’s barrier function is disturbed, allergens, irritants, pollutants and micro organisms can penetrate the skin more easily.
Sensitive skin is not always related to dryness. In either case, it is important to avoid skin care products that contain irritating ingredients such as perfumes and colourants. Always check that the product is dermatologically tested on sensitive skin. Read more about sensitive skin in general or specifically on face or body.
Attention
If you are worried or unsure about your symptoms, or they are becoming worse, we recommend you see your doctor or dermatologist for a face-to-face consultation.
If you need further information to help you identify the cause of your skin complaint, and which treatment route to take, the skin test may be a useful diagnostic tool.
Causes & Triggers


Environmental
- Harsh weather conditions - hot, cold and dry air.
- Seasonal changes - symptoms of dry skin often worsen during either the winter or summer.
- Ultraviolet (UV) light can increase the rate of skin ageing, and skin becomes more prone to dryness as it ages. Read more about age-induced dryness.
Skin care
- Frequent washing, or long, hot baths or showers, removes the lipids that make up the skin barrier.
- Inappropriate skin care routine – It is important to follow a routine, and use products, that are suitable for dry skin. It is especially important not to use strong soaps that strip away natural skin lipids.
Medication
Certain medications and medical treatments (as radiation therapy, dialysis or chemotherapy) are known to cause dry skin as a side effect. Medications that control blood pressure, known as diuretics, are known to have this side effect.
What causes dry skin?
Dry skin is caused by both exogenous (external) and endogenous (internal) factors. A person may be affected by more than one of these factors, and the severity of dry skin will increase with the number of compounding causes. An understanding of which factors influence dry skin will help with the prevention and treatment of dry skin.

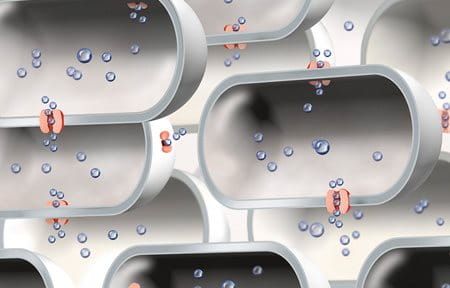
The evaporation of moisture and important substances that trap and bind moisture in the skin is due to a deficiency in these hygroscopic (water-binding) substances, which occur naturally in the skin (natural moisturising factors, NMFs).
The first step in the moisture loss process is the loss of surface lipids that form a natural barrier on the skin to prevent water evaporation.
Once this lipid barrier is broken, moisture can evaporate and the vital moisture-binding substances are easily washed out. As these natural moisturising factors are missing, the skin cannot hold as much water and becomes dry. If this condition persists, the moisture networks in the deeper layers of the skin can become compromised, reducing the natural upward flow of moisture into the upper layers, resulting in very dry skin.
External triggers
External triggers compromise the natural skin barrier, thereby initiating the moisture-loss process.
The main external triggers are:
Attention
Always check with a doctor or pharmacist if you are concerned that a medication may be contributing to dry skin.
Contributing Factors
Factors that can contribute to dry skin
Healthy skin is well-moisturised with an intact skin barrier. The main contributing factors of dry skin are discussed above; however, several other factors also affect the severity of dry skin.
Lack of effective treatment
Lack of effective treatment can also contribute to the severity of the dryness. When dry skin is not treated properly, the dryness can progress and negatively influence the moisture network in the deeper layers. Therefore, a moisturiser that also addresses this fact would help to improve symptoms. Most moisturisers only work to restore the surface barrier function and rely on the moisture network below to supply the moisture to the upper layers.


Sun exposure
Excessive sun exposure can also contribute to skin dryness. A sunscreen for dry skin should contain moisturising actives in addition to an appropriate Sun Protection Factor (SPF), thus rehydrating the skin. It is also important that the sunscreen, and any other skin care products used on dry skin, do not contain irritating perfumes and colourants, as dry skin, especially dry facial skin, is more prone to irritation than normal skin.
Occupational hazards
Certain occupations can also increase the risk of dry skin. Typically these are occupations that require working in hot or cold conditions (farmer/fisherman), frequent use of detergents (doctor/ nurse/ hairdresser), or exposure to chemicals (mechanic/cleaner).

Dehydration
Skin hydration is dependent on the body’s water balance. This further deprives already dry skin of moisture. Elderly people are prone to dehydration as the sensation of thirst diminishes with age. Drinking the minimum of 1.5 litres of fluids daily is essential for maintaining a healthy skin condition.
Smoking
Nicotine and toxins from cigarette smoke may decrease blood flow significantly, resulting in a decreased metabolic rate within the skin. This means the skin dries out more easily and ages prematurely.
Solutions
What solutions are there for dry skin?
Cleansing dry skin


Cleansing dry body skin
When cleansing dry or very dry skin, it is vital that the cleanser is effective yet gentle enough not to wash away skin´s own lipids. Ideally, it should also be enriched with natural moisturising factors, such as Urea, which lock moisture into the skin. Eucerin UreaRepair PLUS 5% Replenishing Body Wash is a very mild product with added moisturising factors for dry to very dry body skin that gently cleanses without drying out. It is suitable in diabetes and Psoriasis.
Cleansing dry facial skin
Mild cleansing of the face is particularly important as the use of unsuited products can increase dryness, which can contribute to the premature development of fine lines and wrinkles. Eucerin DermatoCLEAN Mild Cleansing Milk contains a very effective yet mild cleansing complex that protects the skin from drying out. Eucerin DermatoCLEAN Clarifying Toner gently removes residues, and can be used morning and evening before applying day or night skin care. Read more about an appropriate face care routine.
Moisturising dry skin


Ideally, moisturisers for dry skin should contain actives such as:
- Urea and Lactate that replenish missing natural moisturising factors, which help to bind moisture in the upper layer of the skin. Being natural skin compounds, Urea and Lactate are non-toxic and non-allergenic, making them well-tolerated, even by people who suffer from extremely dry skin. The minimum recommended concentration of Urea should be 5%. Very dry skin generally requires a higher concentration of Urea and other moisturising factors. The Eucerin Urea range contains a range of 5% and 10% Urea lotions, creams and ointments, with products specially formulated for face, hands, feet and body.
- Gluco-glycerol is a molecule that stimulates the skin’s own moisture network, and therefore helps to support the function of the Aquaporins in the deeper epidermal layers, which in turn enhances the natural upward flow of moisture to the outer layers, ensuring long-lasting hydration. Aquaporins are microscopic water channels that are mainly located in the deeper epidermal layers. They supply moisture to the upper stratum corneum layer of the skin, and are essential for maintaining skin hydration.
- Ceramide-3 helps to repair the lipid barrier, and therefore reduces moisture loss.
Caring for age-induced skin dryness
When skin ages, skin dryness contributes to the premature development of fine lines and wrinkles. Read more about signs, causes and solutions for age-induced dryness. Moisturising becomes even more important as maintaining skin hydration can prevent the development of further wrinkles, especially on the face.
Hyaluronic Acid is a molecule that reduces the appearance of dry lines and wrinkles. Hyaluronic Acid is naturally found in the skin, and is an essential component of connective tissue. It has high water binding capacities, improves skin regeneration, and enhances the diffusion of nutrients. The Eucerin Hyaluron Filler range, consisting of day, night and eye cream is uniquely formulated to lock in moisture and help to synthesise more hyaluronic acid.The Hyaluronic Acid helps to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Attention
If you are worried or unsure which treatment route to take, we recommend you see your doctor or dermatologist for a face-to-face consultation.
Avoiding contributing factors
In addition to having a good cleansing and moisturising routine, avoiding factors that contribute to dry skin is important. This will help to reduce the impact of dry skin and the need for treatment:


- Avoid dry air by spending less time outdoors in hot and cold weather, and by using a humidifier indoors when the heating is on.
- Reduce the time spent in hot water by having quick showers instead of long baths.
- Using gloves when washing dishes will help to avoid hot water and strong detergents.
- Wear clothes made of natural materials like cotton and silk that do not irritate the skin. Wool is natural but can irritate, so direct contact should be avoided.
- Try to use a clothes detergent without dyes or perfumes, as these can remain on the clothes after washing and irritate dry skin.
- Use care products without alcohols, perfumes and colourants to avoid irritation.
- Ensure that you drink adequate amounts of fluids.
Internal factors


Genetic influences
Moisture levels in the skin are partly determined by genetics. Some people are genetically predisposed to dry skin. Even in identical conditions, different people will have different skin types. Fair-skinned individuals seem to be more prone to dry skin than people with darker complexions. Diseases such as Atopic Dermatitis, Psoriasis, Diabetes and Ichthyosis have a genetic predisposition.
Hormonal influences
Hormonal changes, such as pregnancy or menopause, can result in skin becoming dry.
Age
As people get older their skin’s ability to produce sweat and lipids is decreased due to the reduction in the function of sebaceous and sweat glands in the skin. Dry skin and ageing are interrelated, and can form a vicious circle. Read more about age-induced dryness.
Diet
A lack of nutrients, unsaturated fatty acids and vitamins can contribute to dry skin. Vitamin C and E are also involved in maintaining healthy skin.
Read more about factors that influence skin.
Our brand values

We deliver a holistic dermo-cosmetic approach to protect your skin, keep it healthy and radiant.

For over 100 years, we have dedicated ourselves to researching and innovating in the field of skin science. We believe in creating active ingredients and soothing formulas with high tolerability that work to help you live your life better each day.

We work together with leading dermatologist and pharmacist partners around the world to create innovative and effective skincare products they can trust and recommend.