What is Epigenetics?
This fascinating research field connects our behaviors and environment, including diet, physical activity, or exposure to UVA/UVB radiation to our gene activity. For example, exercise frequency and dietary choices can cause epigenetic changes that affect how the body interprets DNA sequences.
They turn specific genes on or off thus controlling their activity rather than affecting the genes themselves. This represents an important mechanism for the regulation of biological processes.
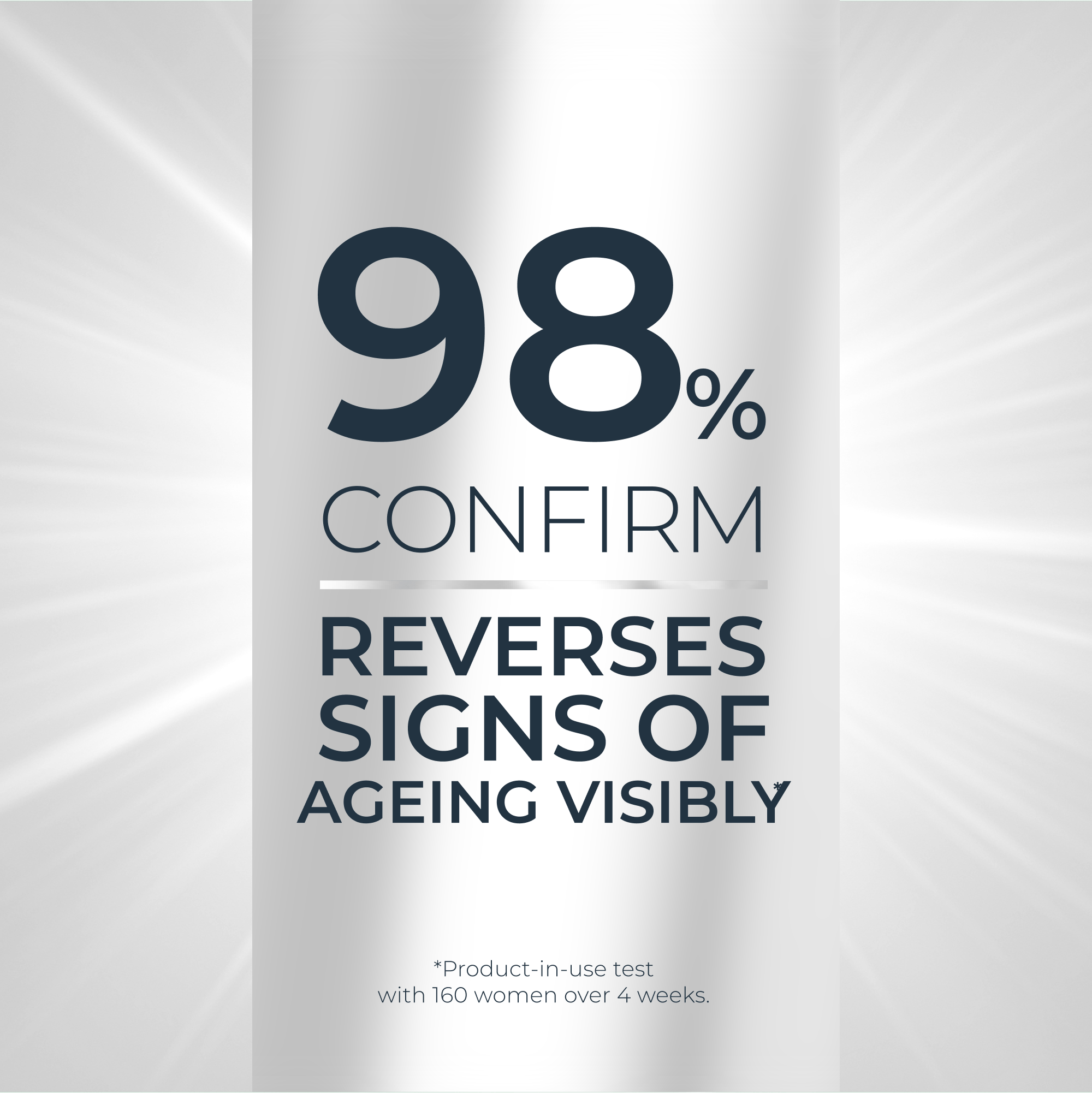
This highlights the connection between our lifestyle choices and genes. By modulating gene expression, these epigenetic changes can significantly affect the condition of our body and our skin. Understanding epigenetics provides valuable insights into how making healthier lifestyle choices, as well as optimising one’s skincare routine can have a positive effect on our genes, and even on how young our skin looks.




.jpg?rx=0&ry=116&rw=1960&rh=431&hash=20E171B57A468E2C473431D8993CA473)